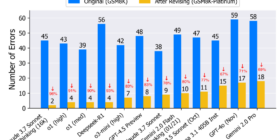
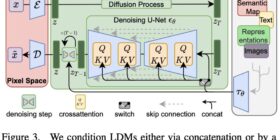
Máquinas hablando entre ellas: Moltbot, Moltbook y la Internet sin humanos
Durante años hemos hablado de asistentes personales basados en inteligencia artificial como si fueran una evolución natural del buscador o del chatbot: herramientas reactivas, relativamente inofensivas, que esperan instrucciones y devuelven respuestas. Lo que está ocurriendo con Clawdbot, Moltbot y ahora OpenClaw rompe ese marco mental de forma bastante más radical. Moltbot es simplemente Clawdbot tras un cambio de nombre forzado por una denuncia de marca registrada de Anthropic, pero nombre aparte, lo importante es entender que no […]