Jina AI Releases Jina-VLM: A 2.4B Multilingual Vision Language Model Focused on Token Efficient Visual QA
Jina AI has released Jina-VLM, a 2.4B parameter vision language model that targets multilingual visual question answering and document understanding on constrained hardware. The model couples a SigLIP2 vision encoder with a Qwen3 language backbone and uses an attention pooling connector to reduce visual tokens while preserving spatial structure. Among open 2B scale VLMs, it reaches state of the art results on multilingual benchmarks such as MMMB and Multilingual MMBench.
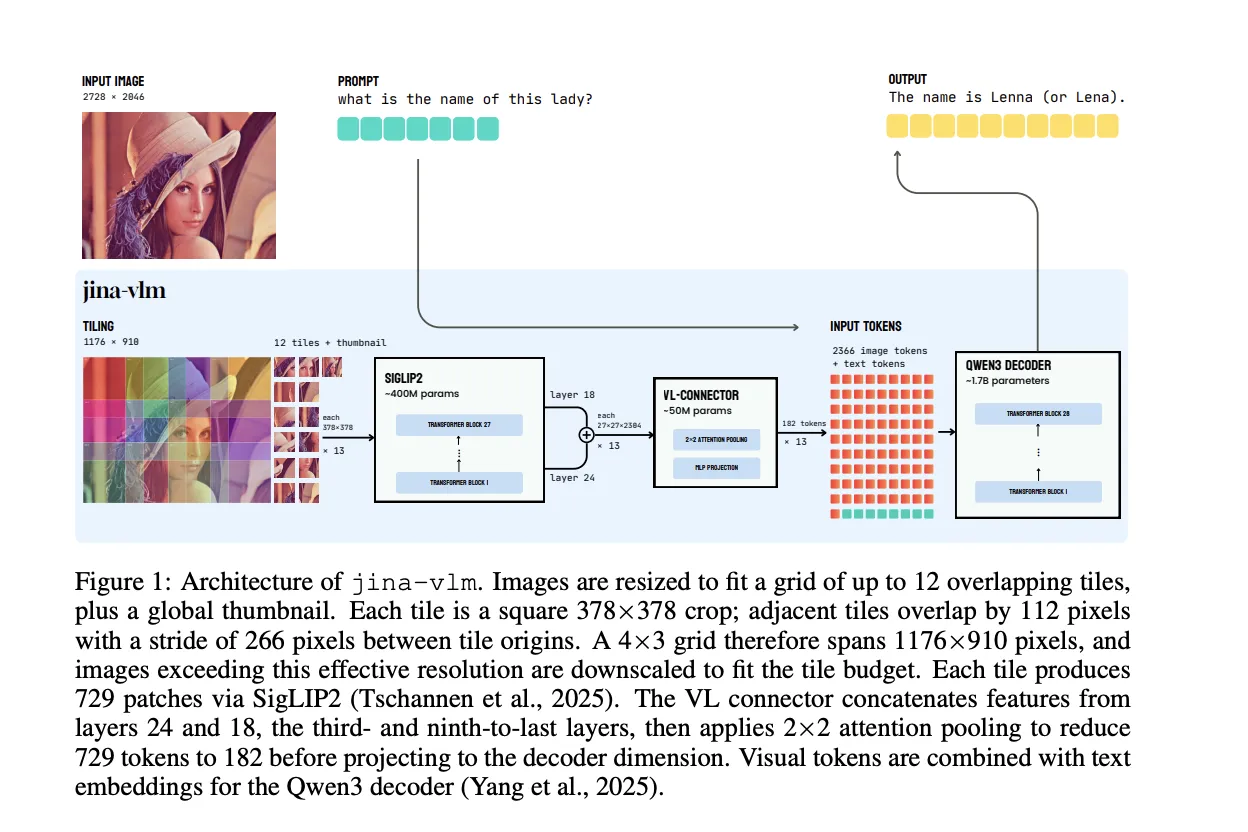
Architecture, overlapping tiles with attention pooling connector
Jina-VLM keeps the standard VLM layout, but optimizes the vision side for arbitrary resolution and low token count. The vision encoder is SigLIP2 So400M/14 384, a 27 layer Vision Transformer with about 400M parameters. It processes 378×378 pixel crops into a 27×27 grid of 14×14 patches, so each tile produces 729 patch tokens.
To handle high resolution images, the model does not resize the full input to a single square. Instead, it constructs a grid of up to 12 overlapping tiles along with a global thumbnail. Each tile is a 378×378 crop, adjacent tiles overlap by 112 pixels, and the stride between tile origins is 266 pixels. A 4×3 grid covers an effective resolution of 1176×910 pixels before downscaling larger images to fit inside the tile budget.
The core design is the vision language connector. Rather than using the final ViT layer, Jina-VLM concatenates features from two intermediate layers, the third from last and ninth from last, that correspond to layers 24 and 18. This combines high level semantics and mid level spatial detail. The connector then applies attention pooling over 2×2 patch neighborhoods. It computes a mean pooled query for each 2×2 region, attends over the full concatenated feature map, and outputs a single pooled token per neighborhood. This reduces 729 visual tokens per tile to 182 tokens, which is a 4 times compression. A SwiGLU projection maps the pooled features to the Qwen3 embedding dimension.
With the default 12 tile configuration plus thumbnail, a naive connector would feed 9,477 visual tokens into the language model. Attention pooling cuts this to 2,366 visual tokens. The ViT compute does not change, but for the language backbone this yields about 3.9 times fewer prefill FLOPs and 4 times smaller KV cache. When including the shared ViT cost, the overall FLOPs drop by about 2.3 times for the default setting.
The language decoder is Qwen3-1.7B-Base. The model introduces special tokens for images, with <im_start> and <im_end> around the tile sequence and <im_col> to mark rows in the patch grid. Visual tokens from the connector and text embeddings are concatenated and passed to Qwen3 to generate answers.
Training pipeline and multilingual data mix
Training proceeds in 2 stages. All components, encoder, connector and decoder, are updated jointly, without freezing. The full corpus contains about 5M multimodal samples and 12B text tokens across more than 30 languages. Roughly half of the text is English, and the rest covers high and mid resource languages such as Chinese, Arabic, German, Spanish, French, Italian, Japanese and Korean.
Stage 1 is alignment training. The goal is cross language visual grounding, not instruction following. The team uses caption heavy datasets PixmoCap and PangeaIns, which span natural images, documents, diagrams and infographics. They add 15 percent text only data from the PleiAS common corpus to control degradation on pure language tasks. The connector uses a higher learning rate and shorter warmup than the encoder and decoder to speed up adaptation without destabilizing the backbones.
Stage 2 is instruction fine tuning. Here Jina VLM learns to follow prompts for visual question answering and reasoning. The mix combines LLaVA OneVision, Cauldron, Cambrian, PangeaIns and FineVision, plus Aya style multilingual text only instructions. The Jina research team first train for 30,000 steps with single source batches, then for another 30,000 steps with mixed source batches. This schedule stabilizes learning in the presence of very heterogeneous supervision.
Across pretraining and fine tuning, the model sees about 10B tokens in the first stage and 37B tokens in the second stage, with a total of roughly 1,300 GPU hours reported for the main experiments.
Benchmark profile, 2.4B model with multilingual strength
On standard English VQA tasks that include diagrams, charts, documents, OCR and mixed scenes, Jina-VLM reaches an average score of 72.3 across 8 benchmarks. These are AI2D, ChartQA, TextVQA, DocVQA, InfoVQA, OCRBench, SEED Bench 2 Plus and CharXiv. This is the best average among the 2B scale comparison models in this research paper from Jina AI.
On multimodal comprehension and real world understanding tasks, the model scores 67.4 on the multimodal group, which includes MME, MMB v1.1 and MMStar. It scores 61.9 on the real world group, which includes RealWorldQA, MME RealWorld and R Bench, and it reaches 68.2 accuracy on RealWorldQA itself, which is the best result among the baselines considered.
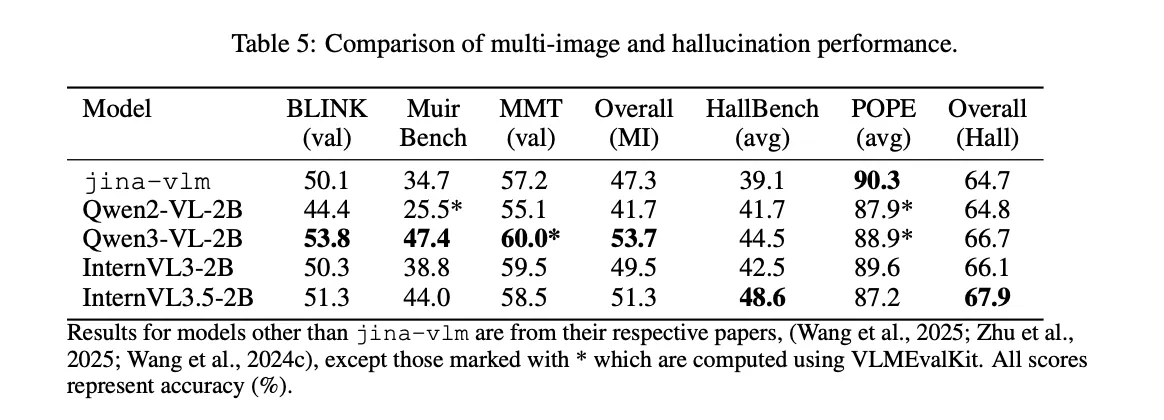
Multi image reasoning is a weaker area. On BLINK, MuirBench and MMT, Jina-VLM reaches an average of 47.3. The research team point to limited multi-image training data as the reason. In contrast, hallucination control is strong. On the POPE benchmark, which measures object hallucination, the model scores 90.3, the best score in the comparison table.
For mathematical and structured reasoning, the model uses the same architecture, without thinking mode. It reaches 59.5 on MMMU and an overall math score of 33.3 across MathVista, MathVision, MathVerse, WeMath and LogicVista. Jina-VLM is comparable to InternVL3-2B on this set and clearly ahead of Qwen2-VL-2B, while InternVL3.5-2B remains stronger due to its larger scale and more specialized math training.
On pure text benchmarks, the picture is mixed. The research team reports that Jina-VLM keeps most of the Qwen3-1.7B performance on MMLU, GSM 8K, ARC C and HellaSwag. However, MMLU-Pro drops from 46.4 for the base model to 30.3 after multimodal tuning. The research team attribute this to instruction tuning that pushes the model toward very short answers, which clashes with the long multi step reasoning required by MMLU Pro.
The main highlight is multilingual multimodal understanding. On MMMB across Arabic, Chinese, English, Portuguese, Russian and Turkish, Jina-VLM reaches an average of 78.8. On Multilingual MMBench across the same languages, it reaches 74.3. The research team reports these as state of the art averages among open 2B scale VLMs.
Comparison Table
| Model | Params | VQA Avg | MMMB | Multi. MMB | DocVQA | OCRBench |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jina-VLM | 2.4B | 72.3 | 78.8 | 74.3 | 90.6 | 778 |
| Qwen2-VL-2B | 2.1B | 66.4 | 71.3 | 69.4 | 89.2 | 809 |
| Qwen3-VL-2B | 2.8B | 71.6 | 75.0 | 72.3 | 92.3 | 858 |
| InternVL3-2B | 2.2B | 69.2 | 73.6 | 71.9 | 87.4 | 835 |
| InternVL3.5-2B | 2.2B | 71.6 | 74.6 | 70.9 | 88.5 | 836 |
Key Takeaways
- Jina-VLM is a 2.4B parameter VLM that couples SigLIP2 So400M as vision encoder with Qwen3-1.7B as language backbone through an attention pooling connector that cuts visual tokens by 4 times while keeping spatial structure.
- The model uses overlapping 378×378 tiles, 12 tiles plus a global thumbnail, to handle arbitrary resolution images up to roughly 4K, then feeds only pooled visual tokens to the LLM which reduces prefill FLOPs and KV cache size by about 4 times compared to naive patch token usage.
- Training uses about 5M multimodal samples and 12B text tokens across nearly 30 languages in a 2 stage pipeline, first alignment with caption style data, then instruction fine tuning with LLaVA OneVision, Cauldron, Cambrian, PangeaIns, FineVision and multilingual instruction sets.
- On English VQA, Jina-VLM reaches 72.3 average across 8 VQA benchmarks, and on multilingual multimodal benchmarks it leads the open 2B scale class with 78.8 on MMMB and 74.3 on Multilingual MMBench while keeping competitive text only performance.
Check out the Paper, Model on HF and Technical details. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter. Wait! are you on telegram? now you can join us on telegram as well.
The post Jina AI Releases Jina-VLM: A 2.4B Multilingual Vision Language Model Focused on Token Efficient Visual QA appeared first on MarkTechPost.