Google announces AI Overviews in Gmail search, experimental AI-organized inbox
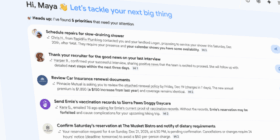
Gmail made us all rethink how email could work when it debuted more than 20 years ago. Google thinks we’re in the process of another email transformation courtesy of AI. The company has unveiled a new round of AI features that will make Gemini an even more integral part of Gmail. The new Gemini experiences are coming to paying subscribers starting today, and a collection of previously premium-only AI features are rolling out widely. AI Overviews first appeared […]
![[Project Showcase] ML-Agents in Python through TorchRL [Project Showcase] ML-Agents in Python through TorchRL](https://www.digitado.com.br/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/s-kmhXhpbCf380Ar8EhkvoJQlmJBbwaYCloj8c0AHU4-cN720d-280x140.jpg)