Empromptu raises $2M pre-seed to help enterprises build AI apps
Empromptu claims all a user has to do is tell the platform’s AI chatbot what they want — like a new HTML or JavaScript app — and the AI will go ahead and build it.

Empromptu claims all a user has to do is tell the platform’s AI chatbot what they want — like a new HTML or JavaScript app — and the AI will go ahead and build it.
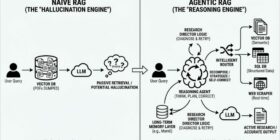
Author(s): AI Rabbit Originally published on Towards AI. Agentic Era If your architecture still looks like “User Query Vector DB LLM,” you aren’t building an AI application; you’re building a hallucination engine. The “naive” RAG era where we just dumped PDFs into Pinecone and prayed for the best is officially over. Here is the technical reality of RAG in 2025.The article discusses the evolution of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines, emphasizing the transition from outdated linear architectures to more […]
submitted by /u/m4moz [link] [comments]

Improvements to roads, bridges, and other infrastructure could take a hit as data center construction accelerates.
submitted by /u/JamesParkes [link] [comments]
An overview of Google’s latest funding announcement for computer science education and the newest AI Quest.
In the wilderness of the New World, the Plymouth Pilgrims had progressed from the false dream of communism to the sound realism of capitalism.

What I’ve learned about making Pandas faster after too many slow notebooks and frozen sessions The post 7 Pandas Performance Tricks Every Data Scientist Should Know appeared first on Towards Data Science.

Synthetic data are artificially generated by algorithms to mimic the statistical properties of actual data, without containing any information from real-world sources. While concrete numbers are hard to pin down, some estimates suggest that more than 60 percent of data used for AI applications in 2024 was synthetic, and this figure is expected to grow across industries. Because synthetic data don’t contain real-world information, they hold the promise of safeguarding privacy while reducing the cost and increasing the […]
This article introduces the Gaussian Mixture Model as a natural extension of k-Means, by improving how distance is measured through variances and the Mahalanobis distance. Instead of assigning points to clusters with hard boundaries, GMM uses probabilities learned through the Expectation–Maximization algorithm – the general form of Lloyd’s method. Using simple Excel formulas, we implement EM step by step in 1D and 2D, and we visualise how the Gaussian curves or ellipses move during training. The means shift, […]